The mosquito genus Aedes on this website also refers to the Ochlerotatus group.
Aedes are found throughout the world. Aedes mosquitoes can carry a variety of pathogens that can be transmitted to humans, including:
- Dengue fever virus
- Chikungunya fever virus
- Yellow fever virus
- Filarial worms
- Eastern equine encephalitis
The larval habitats of Aedes mosquitoes will vary by species, but can be broken down into two main categories:
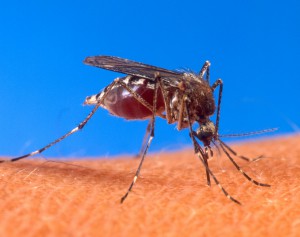
Container mosquito species prefer to lay eggs in artificial containers (e.g., waste tires, flowerpots, gutters, trash cans, etc.) or natural containers (leaf axils, tree holes, etc.) that can hold water. Oviposition takes place just above water level. The species Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus are the primary vectors of concern worldwide, with Aedes aegypti preferring more artificial container types, and Aedes albopictus being more opportunistic and inhabiting both artificial and natural containers.
- Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus
- Other
- Tree hole mosquitoes
- Rock pool mosquitoes

Floodwater mosquitoes lay eggs in wet/moist substrate or waterlogged soil in ground depressions subject to temporary floods. Females differentiate between certain soil types to find the most suitable place for egg laying. Eggs of floodwater mosquitoes remain dormant until they are flooded and conditions are favorable for hatching. Floodwater mosquito populations can even withstand extended dry or cold periods in the egg stage. Select species of floodwater mosquitoes are able to fly long distances to get a blood meal and are aggressive and painful biters.
While floodwater Aedes will lay their eggs in a variety of habitats, these habitats can typically be categorized into four ecotypes:
Floodplain
- General description: Floodplains include low-lying areas along rivers, streams, and lakes that are temporarily inundated at various points in the year. Other low-lying depressions, such as prairie potholes, are floodplains that will hold water following rain events.
- Common floodplain mosquitoes:

Irrigation
- General description: Many species of floodwater mosquitoes have adapted to develop in flood-irrigated habitats including flooded pastures, rice fields, and duck clubs/refuges.
- Common flooded irrigation mosquitoes include:

Woodland
- General description: Woodland pool mosquitoes commonly develop during winter and early spring. Larvae can be found in pools in forested areas following spring snowmelt or rains.
- Common woodland mosquitoes:

Coastal
- General description: Coastal, or saltwater, mosquitoes develop in low-lying plains in coastal areas which include salt marshes, brackish swamps, and dredge spoils.
- Common coastal mosquitoes:

Links to suggested control solutions
Container Aedes:
| VBC Biorational | Container Habitats |
| VectoBac 12AS Teknar SC | Open habitats with minimal vegetation |
| VectoBac WG/WDG |
Floodwater Aedes:
| VBC Biorational | Container Habitats |
| VectoBac WG/WDG (World Health Organization Pesticide Evaluation Scheme [WHOPES] formulation) | Artificial or natural containers |
| VectoBac DT VectoBac 12AS | |
| VectoBac G/GS/GR | Open or vegetated habitats |
| MetaLarv S-PT | Open or vegetated habitats that have dynamic flooding cycles in which pre-flood applications and flood/re-flood capacity is useful |
Quick Links
Contact a Valent BioSciences public health representative.
Contact Us