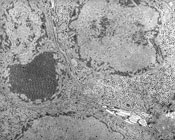
The St. Louis encephalitis virus is a member of the Flaviviridae subgroup and is related to Japanese encephalitis virus. This disease mainly affects the United States, but occasional cases have been reported in Mexico and Canada.
Most St. Louis encephalitis infections produce mild symptoms that include fever and headache. In more severe cases, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, tremors, coma, and convulsions can occur. Fatality rates range from 5%–30%, with the elderly more likely to suffer fatal infections.*
Vector insects
Culex
When Culex mosquitoes become infected with the St. Louis encephalitis virus by feeding on infected birds, they can transmit the virus to humans and animals during the feeding process. Only infected mosquitoes can transmit St. Louis encephalitis virus — once a human has been infected with the virus, it cannot be transmitted directly to other humans. *Source: https://www.cdc.gov/sle/technical/fact.html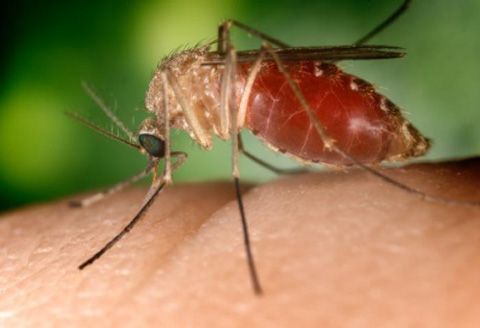
Resources
Learn more about St. Louis Encephalitis Virus disease
Links to vector distribution and habitats
Links to suggested vector-control solutions
Quick Links
Contact a Valent BioSciences public health representative.
Contact Us